
Consulting - Quality
Difference makes the DIFFERENCE
Categorised Menu List
Split a single sheet into Multiple sheets
Conditionally split single sheet into Multiple sheets - Useful at work segregation
Sample Data in picture:
- I used this data to split the data based on Customer Name.
- the same method can be applied where ever there is a duplicate
Examples: when a spread sheet is to be split by bank name or employee name or group name or region name or pin code etc...
Please Note: I have executed the code and placed over here, so, please follow steps give under Sample Code header, and try to execute the program, if it works well, then to read the complete article for understanding as to how it works, else, it is waste of your time.
Let us first consider a situation where you have 10,000 rows, as shown in screen-shot below. The data can be split based on 'Entry Date' Col A or on 'Customer Name' Col B or on 'Customer Number' Col C and so on... ie., in a general situation, where ever we have common data or repeatedly occuring data, we need to split the data.

Procedure to adopt
This can be done in many ways, but, I adopt the following method, which is fairly simple:
- Sort the data (say RawData Sheet) on the required column based on which you want to split
- Write a loop, to check, where, the value in the required column changes. Considering Column B, which is Customer Name Column, The 'Customer Name' changes on 6th, 10th, 13th, 17th, 18th rows respectively.
- Store the value of 'Customer Name' in a variable eg: variable strCustomerName should be 'Arundhati', this should change when the value in the column changes.
- Also, Store the Start Value and End Value in two different variables.
- Select the data between Start Value and End Value
- Create a New Sheet
- Rename the new sheet with Customer Name Variable (strCustomerName)
- Copy the Header Row data from RawData sheet (i.e., first row - if the first row is the header row, always, first row may not the header row) to the current sheet (first row)
- Paste the copied content from RawData sheet onto A2 cell of the new Sheet (assuming - first row in the current sheet, contains header row data from RawData Sheet).
- Repeat the procedure till you encounter the last cell in the RawData Sheet
To Execute the following code,
- Open Ms.Excel (Version I used is 2010), by default, you get three sheets Delete Sheet2 and Sheet3. Rename Sheet1 to RawData, Prepare sample data as shown in the above screen shot,
- Press Alt key (keep Alt key pressed while pressing F11) + F11, You see Visual Basic Editor
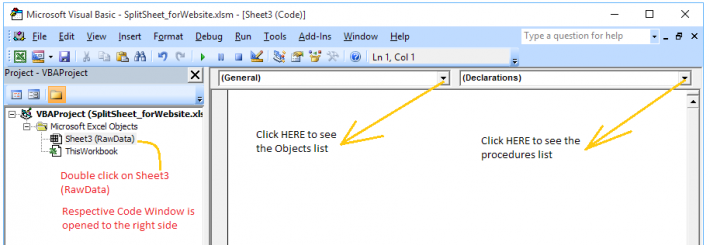
- Double click on 'RawData' Sheet, respective code window opens on right side
- Copy code from this webpage and paste onto the above code widow
- Press Alt + D and L, this will compile the code to check for any errors
- Now, place the cursor in Procedure 1
- Press F8 key constantly, you can check the execution of code.
- Output is as shown below






Points to consider from the above
Option Explicit:
This declaration mandates the program to declare every variable that is used in the programme, may it be integer or long or variant or what ever variable it may be, else System displays an error. This is a good practice, because, variables that are not declared are considered as VARIANT and may, at times, doesnot function as intended.
General or Global Declarations:
The variables declared in this section or after the option Explicit statement are considered Global Variables, they will be available through out the code in the same module. If any variable of the same name is declared inside any procedure (which is called local variable), this variable has more precedence than the global variable. Please refer SCOPE OF VARIABLE topic.
Procedure 1:
cmdRun_Click This activity is for the easy user interface. This is discussed at length, in the article, UserInterface (to be published). for a brief disussion, Place a control on the work sheet, right click on the control, Click on View Code and place this code over there. Now, instead of moving onto code window every time, one can click on the button to execute the program.
I suggest you to practice the same code by doing the same with other different columns over here.
Procedure 2: prcMain:
This is the main procedure from where the program starts and program ends. The program can still work without this procedure but it is advisable for lengthier programs. This is where the basic skeleton of the program resides. Looking into this procedure, we can infer how the program is structured. for additional information on procedures, please refer to Procedures and functions.
Procedure 3: prcDmpGetLastRow:
The code seems to be self explanatory, but for the advantage of the reader: First line Selects and activates 'RawData' worksheet, Goes to the first cell 'A1', from here, it searches for the last cell in the current work sheet, initialises 'lngDmpLastrow' variable with the last row number, initialises 'strDmpLastCell' variable with the last cell address (though we donot use this variable in this program)
Procedure 4: prcSortOnBCN
This procedure is used to sort the data on Customer Name present in Column B. Sorting is done on the entire data set, rather on the Customer Name column. The statement '.SetRange Range("A1:G" & lngDmpLastrow)' where we are assign ing the sort function a range from 'A1' to 'G & lngDmpLastRow', where the value in the variable is substituted and hence looks like '.SetRange Range("A1:G20")' (based on the given sample data) The value in this variable is dependent on the data set you have, if dataset has 10 rows, then 'lngDmpLastRow' will have a value of 10, else if, the dataset has a 1000 rows, then the value in 'lngDmpLastRow' will have a value of 1000. Header Row is considered in the statement '.Header = xlYes', so Header Row will not be part of dataset while on sort, and other parameters like match case, order or sort, and the method of sort are also considered in the same code.
Procedure 5:
prcAddNewSheet This procedure creates a new sheet, created at the end of the current collection, ie, it counts the number of sheets, before the creation of new sheet and adds a new sheet after the highest sheet count value (to put it simply, it appends a new sheet), selects the new sheet and re-names the new sheet with the value in the variable 'newSheet'
Procedure 6:
prcPasteHeaders This procedure creates header row for the newly created sheet. The source for headers is the RawData Sheet. It will retain the format / coloring of the headers and also the column width as it is in RawData Sheet.
Procedure 7:
prcSegregateNewSheets This is the main part of the program, that we intend to work with. The entire program is taken in a loop. The look start with 2, because the first line has header information. This look works till the end, ie., the last row, checks if the next value is equal to the current value, if so, it skips, else, new sheet is created, header row is added, Copies the current selection into A2 cell of the new sheet.
Procedure 8:
prcDeletePrevSheets This procedure is generally called a Clean-Up procedure, where it intends to clear any sheet that is already existing, with exception to the one in the given code. In the given code, it deletes all sheets other than 'RawData' sheet.
Examples for Exercise:
- Segregate the same data on Date
- on Customer Number
- on Statement Line Number
- on Line transaction Code
- on Bank Statement Currency
- on Type - the type of transaction
- Now try to do this segregation on two different columns like: For the Customer_Name and Currency - ie., If a customer has different kinds of transactional currencies eg: Arundhati does transactions on EUR, INR, USD, then there should be three sheets like 'Arundhati-INR', 'Arundhati_EUR', 'Arundhati_USD'
- Now try to enhance the above example based on TYPE of transaction, whether, it is a credit transaction or debit transaction. Now the output sheets will look like 'Arundhati_INR_Debit', 'Arundhati_INR_Credit', 'Vamsi_INR_Credit', 'Vamsi_EUR_Debit' and so on...